
Biopharmaceuticals — from therapeutic proteins to vaccines — rely on recombinant expression systems. Yet one hidden challenge in production is the removal and quantification of host cell proteins (HCPs), which are residual impurities from the production host (e.g. E. coli). Left unchecked, these HCPs can trigger immunogenicity, reduce stability, or complicate regulatory approval.
If you missed our webinar on October 3, 2025 — “Detection of E. coli HCPs” — this blog is your catch-up. Here, we clarify how HCP detection works (especially via sandwich ELISA), explore regulatory expectations, compare methods, and show how deNOVO Biolabs offers a cost-effective, customizable solution tailored for your analytic and QC needs.
Why detect HCPs?
- Safety & Immunogenicity Risk
Residual HCPs in biologics can induce unwanted immune reactions. Even trace levels of immunogenic proteins can lead to adverse effects in patients. - Product Stability & Efficacy
Some HCPs might interact with the therapeutic protein (e.g. binding, aggregation, degradation), degrading product stability or altering activity. - Regulatory Compliance & Market Access
Regulatory authorities (FDA, EMA, ICH, WHO) expect companies to monitor and control HCP levels in final drug substance and intermediates. Failure to provide robust HCP data may delay approval. - Process Control & Optimization
In development, understanding how HCP levels change across purification steps guides process improvements (e.g. chromatography optimization). An accurate assay becomes essential.
Because of these reasons, an HCP detection assay is a foundational element in any biologics QC toolbox.
Methodologies for HCP Detection:
ELISA, MS & More
While multiple techniques exist, each has pros and limitations. Below is a succinct comparison.
1. Sandwich ELISA (the industry standard)
- In a sandwich ELISA, a capture (anti-HCP) antibody is immobilized on a plate, sample is added, then a detection antibody binds the captured HCP, followed by an enzyme-linked readout (e.g. HRP).
Wikipedia+2Cytiva+2 - It is widely used because it’s sensitive, relatively low cost, automatable and fits GMP workflows.
cygnustechnologies.com+2lonza.com+2 - However, one key challenge is antibody coverage: the polyclonal antibodies used must recognize as many HCP species as possible. Gaps in coverage can lead to underestimation.
ProtaGene+2info.bioanalysis-zone.com+2 - ELISA alone cannot always identify which individual HCPs remain; it provides a bulk quantification.
ProtaGene+2info.bioanalysis-zone.com+2
Researchers have also developed hybrid methods such as Immuno-affinity extraction (IAC) paired with mass spectrometry (IAC-MS) to evaluate immunoreagent coverage and detect HCPs missed by ELISA.
ProtaGene+1
2. Mass Spectrometry (MS) / Proteomics-based methods
- MS delivers molecular-level identification and quantification of individual HCPs in a sample, including low-abundance ones that ELISA might miss.
info.bioanalysis-zone.com+2ProtaGene+2 - It is often used as an orthogonal / complementary approach to ELISA, especially during process development or risk assessment.
BioProcess International+3ProtaGene+3info.bioanalysis-zone.com+3 - The caveat: MS workflows tend to be more complex, require advanced instrumentation and data interpretation, and can be costlier relative to routine ELISA.
info.bioanalysis-zone.com+2ScienceDirect+2
3. Other supporting methods
(SDS-PAGE, Western blot, 2D-PAGE)
These are often used for qualitative or semi-quantitative assessments, verifying coverage or detecting particular HCP bands, but lack the quantitation precision needed for regulatory release testing. ProtaGene+3Cytiva+3info.bioanalysis-zone.com+3
In modern workflows, ELISA + MS (orthogonal) is a balanced strategy: ELISA gives robust quantitation for routine control, while MS helps you detect gaps and confirm safety-related HCPs.
Step-by-Step working of E. coli HCP ELISA
Here’s a simplified walk-through, consistent with what we covered in our webinar:
- Capture Antigen (Antibody) Immobilization
The microtiter plate wells are coated with a polyclonal anti-E. coli HCP antibody (capture), which anchors potential HCPs when the sample is added. - Sample Loading
Your test sample (fermentation supernatant, downstream intermediate, or final product) is added. HCP molecules, if present, bind to the immobilized capture antibody. - Washing
Unbound proteins (including many non-HCPs or weakly binding ones) are washed away through buffer washes, improving assay specificity. - Detection / Reporting Antibody Binding
A second biotinylated anti-HCP polyclonal antibody (reporting antibody) is added, which binds to the captured HCP, forming a “sandwich.” - Signal Generation & Readout
A streptavidin-HRP conjugate is then applied, which binds to the biotin on the reporting antibody. Substrate (e.g. TMB) is added and a color change is measured (usually at 450 nm), creating a signal proportional to the HCP level. abcam.cn+2Cytiva+2 - Quantification via Standard Curve
The optical density (OD) readings are mapped to known standard concentrations to derive HCP concentration in the sample. Proper blank subtraction and dilution correction are applied.
Each step must be optimized (incubation times, buffer composition, blocking, washing rigour) to ensure sensitivity, low background, and linear response across the range.
Regulatory Landscape & Best Practices
Understanding HCP detection is not just a lab exercise — it must align with global regulatory expectations.
- Regulatory Guidelines:
US FDA, EMA, ICH, and WHO typically require product- or process-specific validation of HCP assays. Blanket thresholds (e.g. 1–100 ng HCP per mg of product) are often cited, but regulators expect demonstration of relevance to your specific molecule and process. (This was a major point in our webinar.) - In our discussion, Dr. Dinesh and Dr. Manjunath underlined that product-specific evaluation is emphasized more than adopting a single global standard.
- Consistency Across Guidelines:
While regulatory texts may have different formats, the underlying principles — sensitivity, precision, specificity, robustness, and stability — are broadly aligned. - Instrument Compliance:
For data validity, equipment like plate readers must conform to CE certification and 21 CFR (Part 11) for electronic records. - Emerging Standards:
Even in December 2024, USP released General Chapter <1132.1> on “Residual Host Cell Protein Measurement by MS” to promote standardized MS approaches and strengthen impurity profiling demands. BioProcess International - Regulators increasingly ask for orthogonal assays (like MS) to confirm ELISA coverage or detect “blind spots.” BioProcess International+2info.bioanalysis-zone.com+2
In short: you need an HCP method that is scientifically sound, validated in context, and supported by robust instrumentation.
deNOVO Biolabs’ E. coli HCP ELISA solution
At deNOVO Biolabs, we do not just talk theory — we deliver actionable, high-quality tools. From our webinar:
- Our E. coli HCP ELISA kit offers a dynamic range of 2–500 ng/mL and 1 ng/mL sensitivity — fully competitive with imported kits.
- We’ve achieved low intra-batch precision (<10%) and inter-batch variability (<20%), in line with regulatory expectations.
- Antibodies are raised across multiple E. coli strains, giving 80–85% coverage and reactivity across the typical impurity spectrum.
- We offer custom assay development (antibody generation, kit assembly, validation) delivered in 6–8 months.
- For regulatory compliance, our validations align with EMA guidelines, ensuring performance across sensitivity, precision, accuracy, stability.
- We also affirm that the instruments used (plate readers, etc.) comply with CE and 21 CFR standards — giving confidence in data integrity.
- When asked technical queries (e.g. upper/lower limits derivation), we commit to sharing full technical documentation to assist your regulatory submission.
In effect, deNOVO’s offering is positioned as a cost-effective, sensitive, customizable, and regulatory-alignedalternative to expensive imported kits — while preserving scientific rigor.
Challenges & Solutions
Knowing the pitfalls helps you implement better assays. Here are common challenges — and how deNOVO addresses or helps you mitigate them:
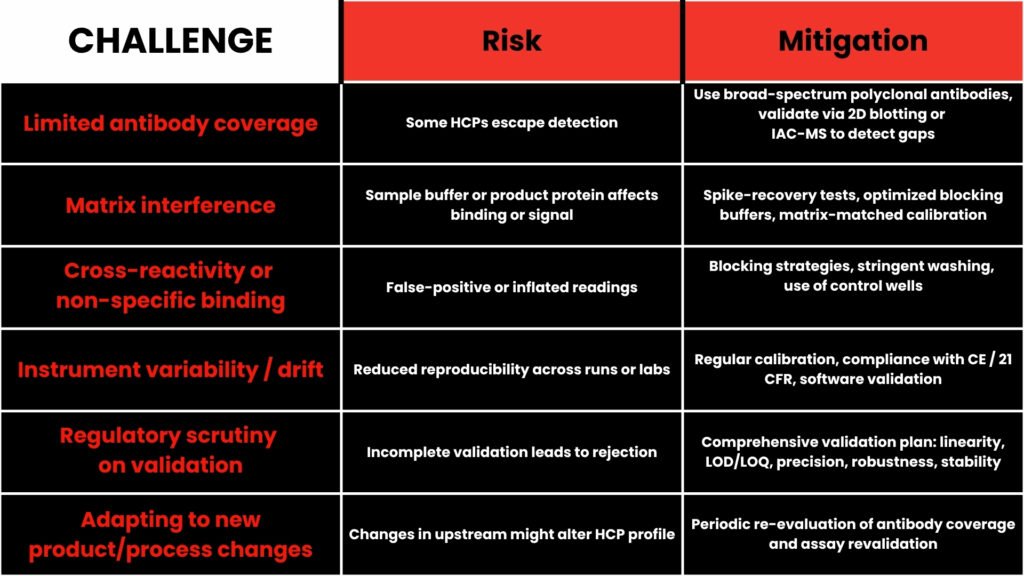
At deNOVO, our technical support offers guidance on these aspects — you don’t have to navigate them alone.
How can your Team benefit?
- Process Development & Optimization
Monitor how purification steps (e.g. protein A, ion exchange) reduce HCP burden; tweak buffer conditions or chromatography parameters based on HCP trends. - Release & QC Testing
Run the deNOVO ELISA kit for lot release consistency checks with validated sensitivity, precision, and compliance-ready data. - Risk Assessment & Regulatory Submission
Use this data — backed by documentation — to support safety claims, impurity limits, or comparability studies. - Custom Product-Specific Assays
If your target molecule or host strain has atypical HCPs, deNOVO can build a bespoke assay to capture your unique impurity profile.
How to deploy this knowledge?
- Set your HCP strategy early
Decide whether to use a generic kit or invest in a process-specific assay. Review immunocoverage requirements. - Conduct pilot evaluation
Run preliminary ELISAs, check spike recovery, linearity, background levels, and cross-reactivity. - Validate comprehensively
Perform full validation: precision, accuracy, LOD/LOQ, robustness, stability, dilution linearity. - Complement with orthogonal methods
Use MS (IAC-MS or LC-MS/MS) to check for undetected HCPs in your final product or process intermediates. - Document method & metrics
Maintain paperwork on instrument compliance (CE, 21 CFR), validation reports, coverage analysis, and change control. - Monitor continuously
After method integration, track assay performance, drift, and any process changes that may affect HCP profile. - Engage with vendors / partners
Work with trusted providers (like deNOVO) to adapt or upgrade the assay, or seek technical support when anomalies arise.
Interested in a high-performing E. coli HCP ELISA kit or custom assay designed for your product?
Contact deNOVO Biolabs today to get a consultation, request our technical datasheets, or start a pilot assay.📧 Email us: info@denovobiolabs.com
🌐 Website / Quote Request: www.denovobiolabs.comWe’ll guide you through feasibility, timeline (6–8 months for custom builds), validation support, and regulatory readiness.
Conclusion
If you missed our October 3rd webinar, here is the recap:
- HCP detection is essential for safety, stability, regulatory compliance, and process optimization.
- Sandwich ELISA remains the industry workhorse — but its reliability depends on antibody coverage, method optimization, and validation.
- Mass spectrometry and other orthogonal approaches help you verify coverage and catch potentially dangerous outliers.
- The evolving regulatory landscape (e.g. USP <1132.1>) is pushing for more rigorous impurity profiling and standardized MS methods.
- deNOVO Biolabs offers a competitive, sensitive, customizable E. coli HCP ELISA platform — with proven metrics, regulatory alignment, and technical support for your team.
If you are in R&D, QC, or regulatory affairs, a robust HCP strategy is a foundational pillar for biologics success. Don’t settle for generic kits that may leave your product exposed — partner with experts who provide transparency, flexibility and validated performance.
